MHTML stands for MIME HTML (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions Hypertext Markup Language), which is a html page archive format initially created for Microsoft Internet Explorer by Microsoft. A mhtml file contains all the required media for displaying a web page in one single file, which makes transmitting the web page archive by email much easier. The extension of mhtml is “mht” and a mhtml file is also called a mht file. EMF is the extension name of an image file stored in format of Enhanced MetaFile. EMF is a version upgraded format of WMF (Windows MetaFile), which is 32-bit and has more commands than WMF.
The VeryPDF HTML Converter Command Line supports to convert a document of mhtml to emf image by storing the converted image in vector mode. In the MS-DOS command line prompt window, the commands as follows will complete the conversion from mhtml to emf,
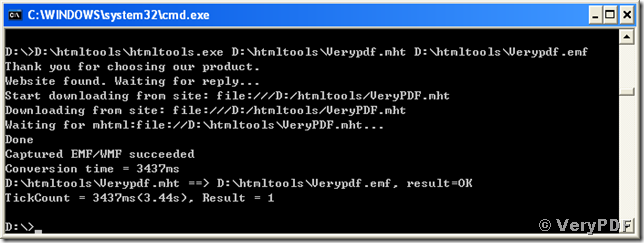
D:\htmltools\htmltools.exe D:\htmltools\Verypdf.mht D:\htmltools\Verypdf.emf <Enter>.
The command “D:\htmltools\htmltools.exe” calls the executable component of the conversion tool, “D:\htmltools\Verypdf.mht” points to the source document, and “D:\htmltools\Verypdf.emf” specifies the output file path, name and target format for the conversion. If your MS-DOS command prompt is running in the directory where the VeryPDF HTML Converter Command Line is installed in, the path “D:\htmltools\” in the first command calling the converter is not necessary.
Here is the process in the screen snapshot.
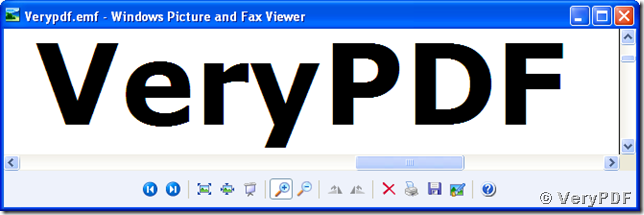
The following snapshot shows a zoomed-in image converted from mhtml to emf stored in vector, which shows that the clarity and quality of image are not lost in the zooming operation.