CHAPTER 3
130
Syntax
Public-Key Encryption Algorithms
PKCS#7 object is designed to encapsulate and encrypt what is referred to as the
enveloped data.
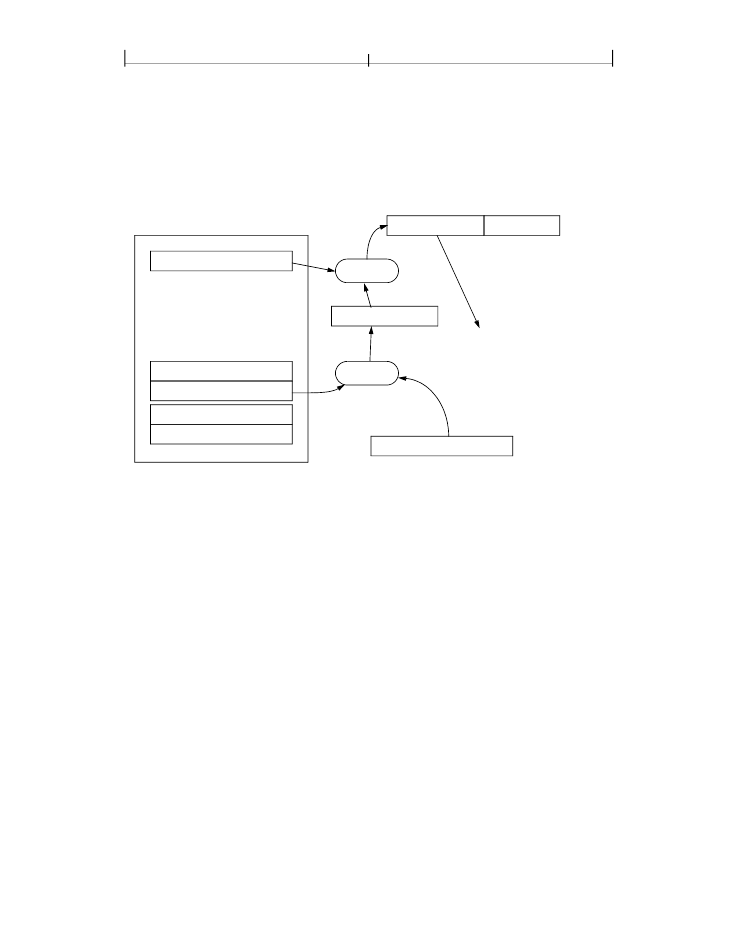
PKCS#7 Object
Enveloped data
Plaintext byte array
20-byte seed Permissions*
* Permissions not present
when PKCS#7 object is ref-
erenced from Crypt filter
decode parameter dictio-
nary
Decrypt
Plaintext key
Used to generate
encryption key as
described on page
John Doe
Encrypted key
Jeff Smith
Encrypted key
Decrypt
John Doe’s private key
FIGURE 3.4
Public-key encryption algorithm
The enveloped data in the PKCS#7 object contains keying material that must be
used to decrypt the document (or individual strings or streams in the document,
when crypt filters are used; see Section 3.5.4, “Crypt Filters”). A key is used to
encrypt (and decrypt) the enveloped data. This key (the
plaintext key
in Figure
in the PKCS#7 object (as the
encrypted key
for each recipient). To decrypt the
document, that key is decrypted using the recipient’s private key, which yields a
decrypted (plaintext) key. That key, in turn, is used to decrypt the enveloped data
in the PKCS#7 object, resulting in a byte array that includes the following
information:
•
A 20-byte seed that is used to create the encryption key that is used by Algo-
rity handler that encrypted the document.
•
A 4-byte value defining the permissions, least significant byte first. See